Building Scalable and Interoperable Digital Solutions Using ODA
Open Digital Architecture (ODA) is a cutting-edge business and technology architecture crafted to meet the evolving needs of telecoms and digital service providers.
In an era of digital transformation, ODA enables telecoms and digital service providers to stay competitive, reduce complexity, and drive innovation while improving cost efficiency. It does so by facilitating the creation of digital services through reusable, interoperable software blocks that run natively in the cloud.
“ODA is crucial for creating more value for customers and staying ahead of the competition. It accelerates time to market, simplifies integrations within the digital ecosystem, and enhances customer experience and engagement management. By incorporating intelligent ODA Components, such as anomaly prediction and detection, ODA enables a shift from traditional BSS/OSS architecture to a modern DSS architecture.”—Luqman Shantal, CEO at Makman.
Foundational to the ODA are:
- ODA Components: Reusable and interoperable software blocks used to build digital services
- ODA Component Directory: Where you can find and procure ODA Components
- ODA Canvas: Where you can deploy, run, and test ODA components
Together, these three elements provide a holistic and interoperable framework for building, deploying, and managing digital business solutions. This article explores each element in detail and examines how they integrate seamlessly.
ODA Components
At the heart of ODA are its reusable software blocks, known as ODA Components. These components serve as building blocks for crafting digital services. The ODA Component are ① Reusable, ② Modular, ③ Standardized, and ④ Machine-readable software components.
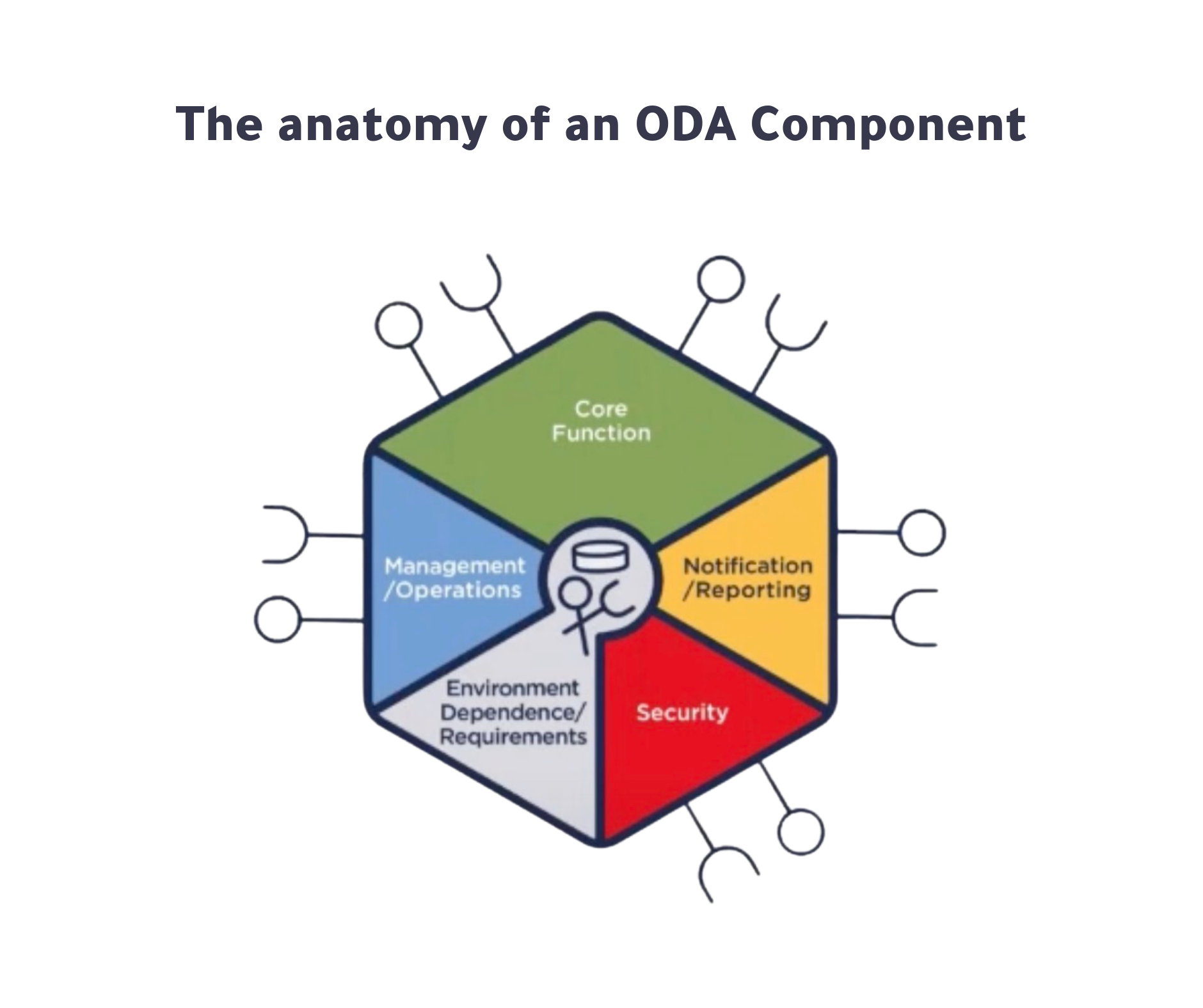
Represented visually by a hexagon (Check the following image), each ODA component conveys key information about its functionalities and operations:
- A green rhombus at the top illustrates the functional scope (i.e. the core function of the component, for example: the function of the component could be “Bill Generation Management”)
- Lollipops extending from the hexagon edges symbolize the Open APIs exposed by the component.
- Other colored segments within the hexagon highlight aspects such as security, observability, and operational management.
ODA components are developed through the ODA Components & Canvas collaboration project, where TM Forum members work together to set standards and drive innovation.
The ODA Component Directory
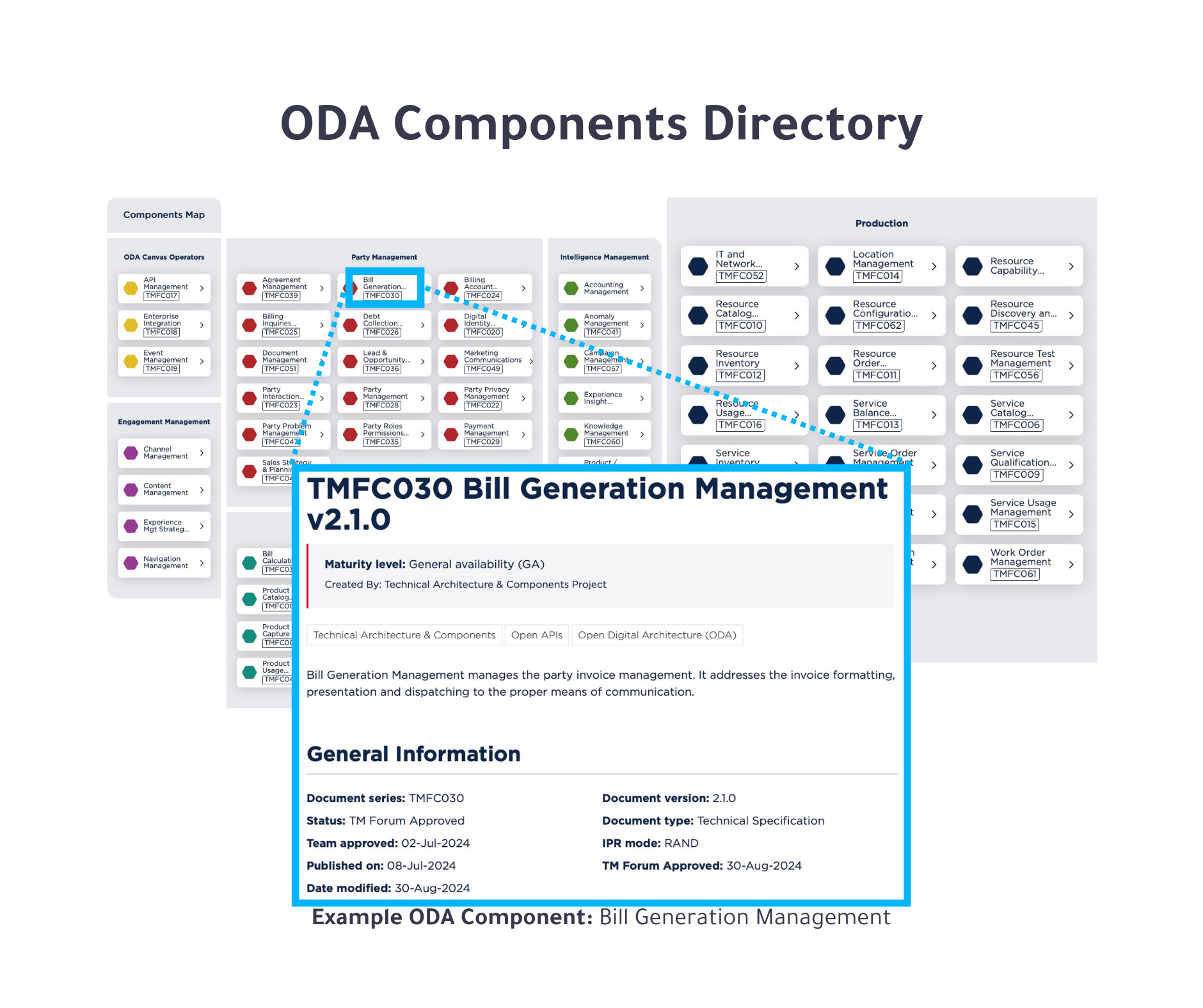
The ODA Component Directory serves as a repository and marketplace for exploring and procuring ODA Components. It acts as a bridge between buyers and software providers, ensuring that components meet the stringent requirements of plug-and-play interoperability within a standardized deployment environment, the ODA Canvas (explained in the next section).
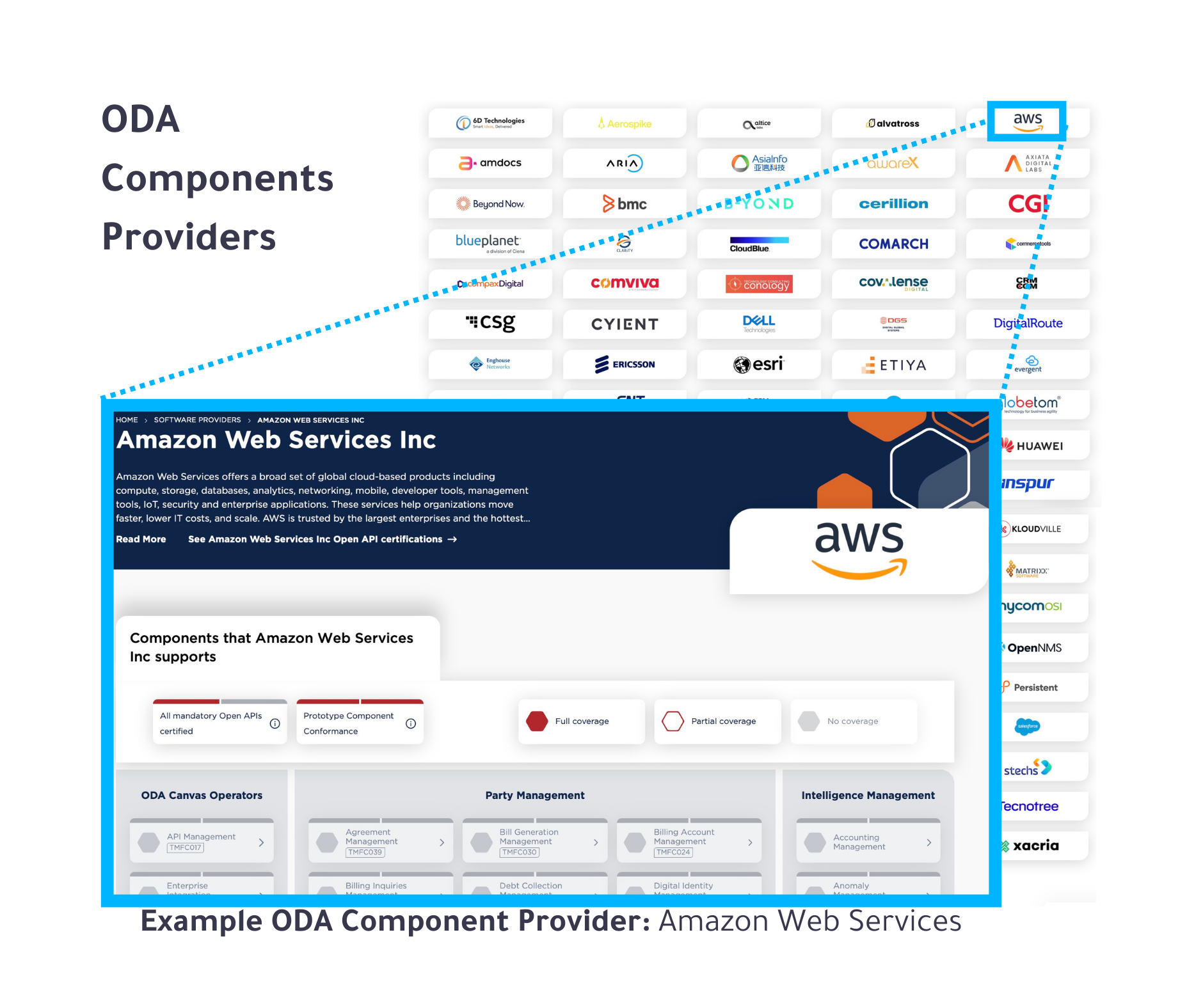
Buyers (i.e., CSPs or DSPs) can search the ODA Component Directory by a specific component OR component provider/ vendor, access metadata, review API exposure, and evaluate vendor details, including conformance levels. Refer to the following two images for a preview of the directory’s interface.
To maximize the utility of the ODA directory:
- Identify the necessary ODA components by reviewing their specifications and functional mappings.
- Check open API certifications for insights into vendor deployments.
- Reference certification data in your RFPs and use it as an acceptance criterion for transformation projects.
- Encourage vendors to achieve level 1 conformance and list their products in the directory.
For more details, visit the ODA Component Directory or the ODA Software Providers Directory.
The ODA Canvas
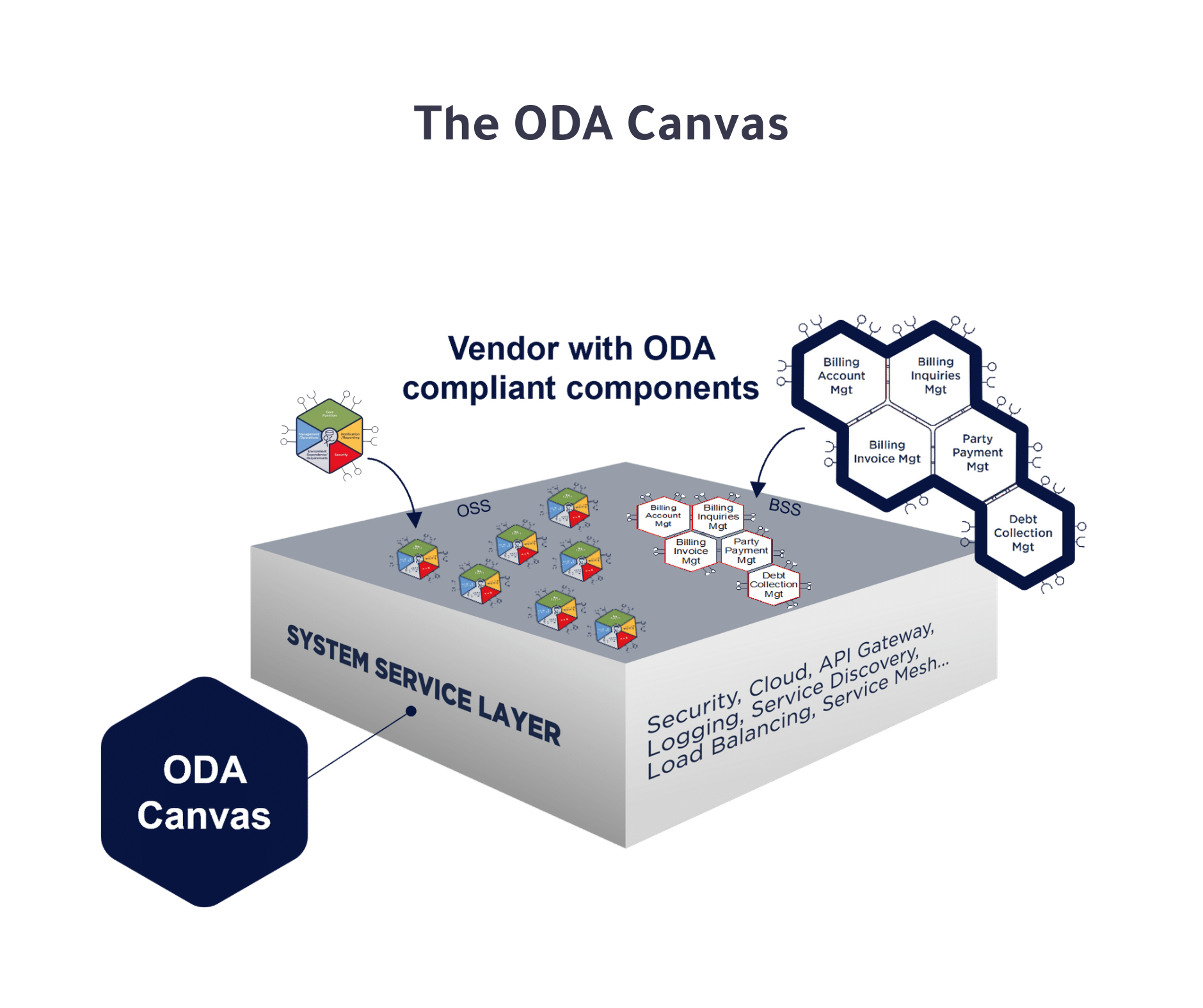
The ODA Canvas delivers an automated operational platform for running ODA components. Its primary mission is to provide:
- Tools and frameworks for CSPs and DSPs to establish a standardized deployment environment using the ODA Canvas.
- A mechanism for vendors to deliver ODA Components that seamlessly integrate into the Canvas.
Set to launch for general availability in January 2025, the Canvas is already being used by CSPs and cloud platforms to integrate and deploy ODA components. One of its key features is its ability to enable workload portability across different cloud environments. Leading cloud providers, such as Google and Microsoft, are making significant contributions to the reference Canvas through the TM Forum’s Innovation Hub. Meanwhile, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has developed its own ODA-compliant Canvas but has not yet joined the Hub.
As more CSPs adopt the Canvas, hyperscalers plan to offer prebuilt versions through their marketplaces, simplifying deployment for digital service providers without proprietary solutions.
Getting the ODA Canvas:
The Reference Implementation of the ODA Canvas, also called “Canvas in a Bottle,” is deployable on the Kubernetes platform and available for download. It can be set up locally and is designed for simplicity, requiring minimal experience with Kubernetes. The implementation also includes TM Forum Open API references to speed up application development. You can access it through GitHub.
The Reference Implementation, also known as Canvas in a Bottle, can be accessed via GitHub.
By leveraging Open Digital Architecture—through its Components, Component Directory, and Canvas—telecom and digital service providers can achieve new levels of scalability, interoperability, and growth in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
Copyright disclaimer: All images and terminology used are copyrighted by TM Forum. This article is based on publicly available content and resources from the TM Forum website. You can access more resources by becoming a member of the TM Forum.